Description
Given a binary search tree and a node in it, find the in-order successor of that node in the BST.
The successor of a node p is the node with the smallest key greater than p.val.
Example
Example 1:1
2
3Input: root = [2,1,3], p = 1
Output: 2
Explanation: 1's in-order successor node is 2. Note that both p and the return value is of TreeNode type.
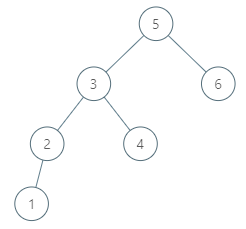
Example 2:1
2
3Input: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,null,1], p = 6
Output: null
Explanation: There is no in-order successor of the current node, so the answer is null.
Note:
- If the given node has no in-order successor in the tree, return null.
- It’s guaranteed that the values of the tree are unique.
Solution
Solution 1: Basical Solution, O(h);1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
// Solution 1: basic one, O(h)
public TreeNode inorderSuccessor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p) {
if (root == null) return null;
TreeNode res = null;
if (p.right != null){
p = p.right;
while(p.left != null){
p = p.left;
}
return p;
}
while(root != p){
root = (p.val > root.val) ? root.right : (res = root).left;
}
return res;
}
}
Solution 2: Improved solution, O(h)1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
// Solution 2: more improved, O(h)
public TreeNode inorderSuccessor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p) {
TreeNode res = null;
while(root != null){
root = (root.val > p.val) ? (res = root).left : root.right;
}
return res;
}
}