
Description
You are given a doubly linked list which in addition to the next and previous pointers, it could have a child pointer, which may or may not point to a separate doubly linked list. These child lists may have one or more children of their own, and so on, to produce a multilevel data structure, as shown in the example below.
Flatten the list so that all the nodes appear in a single-level, doubly linked list. You are given the head of the first level of the list.
Example
1 | Input: |
Explanation for the above example:
Given the following multilevel doubly linked list:
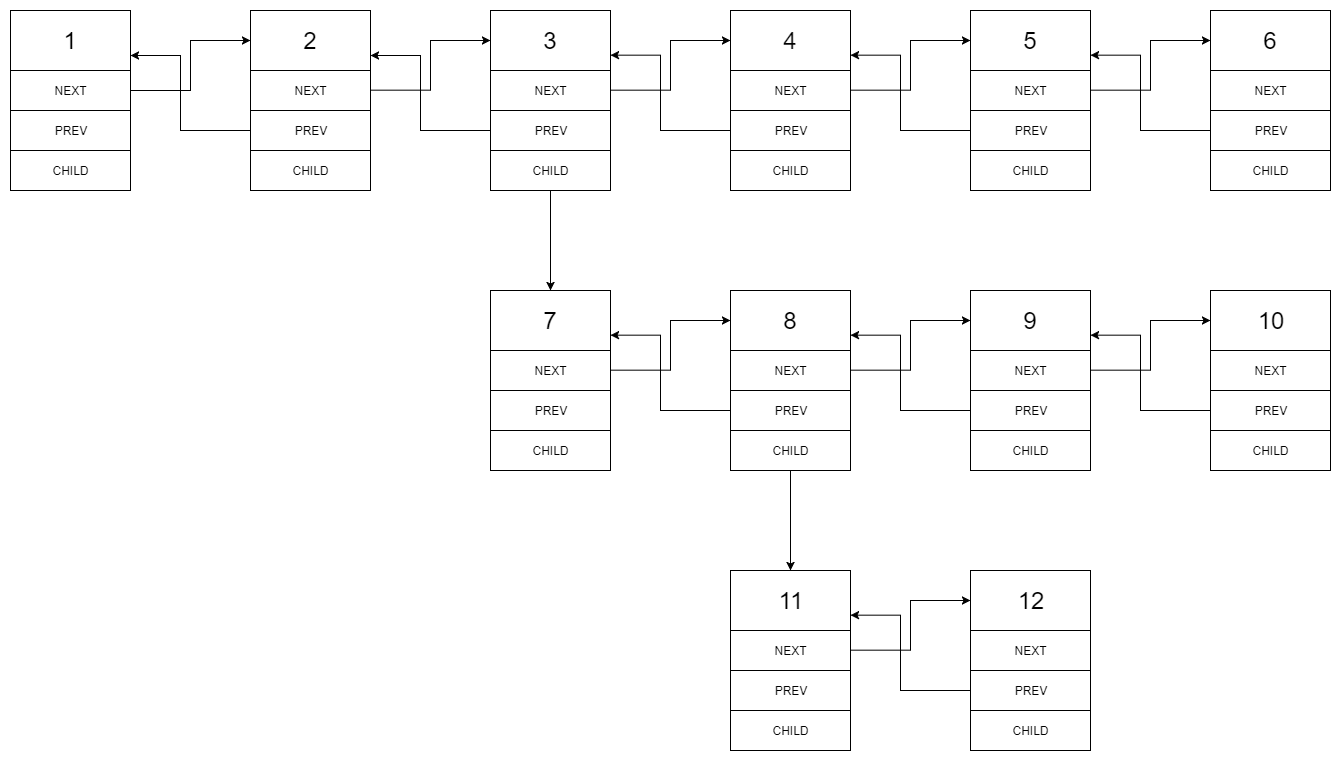
We should return the following flattened doubly linked list:

Solution
Method 1: Iteration1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public int val;
public Node prev;
public Node next;
public Node child;
public Node() {}
public Node(int _val,Node _prev,Node _next,Node _child) {
val = _val;
prev = _prev;
next = _next;
child = _child;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public Node flatten(Node head) {
if (head == null) return head;
Node p = head;
while( p != null){
if (p.child == null){
p = p.next;
continue;
}
else{
Node childTail = p.child;
while(childTail.next != null) childTail = childTail.next;
childTail.next = p.next;
if (p.next != null) p.next.prev = childTail;
p.next = p.child;
p.child.prev = p;
p.child = null;
p = p.next;
}
}
return head;
}
}
Mathod 2: Recursion1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public int val;
public Node prev;
public Node next;
public Node child;
public Node() {}
public Node(int _val,Node _prev,Node _next,Node _child) {
val = _val;
prev = _prev;
next = _next;
child = _child;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public Node flatten(Node head) {
if (head == null) return null;
helper(head);
return head;
}
private Node helper(Node cur){
if (cur == null) return cur;
if (cur.child == null){
if (cur.next == null) return cur;
return helper(cur.next);
}
else{
Node child = cur.child;
cur.child = null;
Node next = cur.next;
Node childTail = helper(child);
cur.next = child;
child.prev = cur;
if (next != null){
childTail.next = next;
next.prev = childTail;
return helper(next);
}
return childTail;
}
}
}